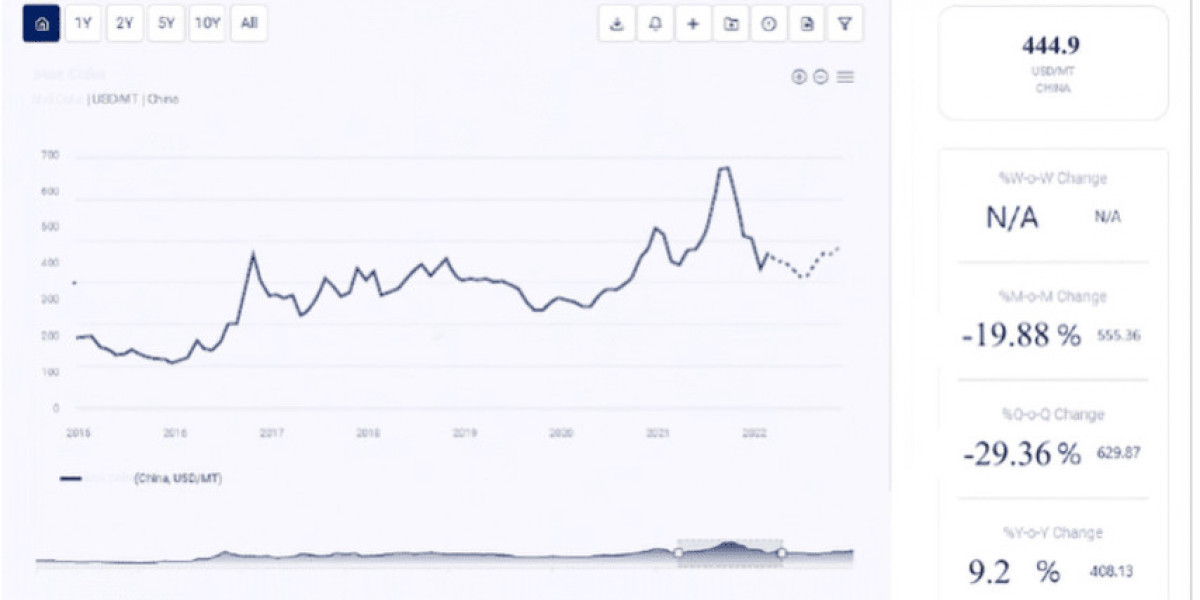
Melons, including varieties such as watermelon, cantaloupe, and honeydew, are some of the most popular and refreshing fruits enjoyed worldwide. Their high water content and sweet, refreshing taste make them a favourite during the warmer months. Like many other agricultural products, melon prices fluctuate depending on various factors including weather conditions, market demand, and production levels. Understanding these price trend of melon is crucial for producers, consumers, and distributors alike. In this article, we will explore the factors that influence melon prices, review historical trends, and provide insights into the future outlook for melon markets globally.
1. Key Factors Affecting Melon Prices
The price of melons is influenced by several internal and external factors that can cause fluctuations throughout the year. The main drivers include weather conditions, supply chain challenges, seasonal demand, and consumer preferences.
1.1 Weather Conditions and Climate Impact
Melons are sensitive to weather patterns, and their price is often impacted by both short-term and long-term changes in climate. Extreme weather events such as droughts, floods, and frosts can negatively affect melon crops, leading to reduced yields and higher prices.
Temperature Sensitivity: Melons require warm temperatures for optimal growth. Too much rain or extreme heat can harm fruit quality and reduce the overall harvest, resulting in a supply shortage and higher prices.
Seasonal Variations: Melon prices tend to peak during the summer season when demand is highest due to their refreshing qualities. However, regional differences in harvest periods can lead to price fluctuations throughout the year. For example, melons produced in the Southern Hemisphere may be harvested during months when Northern Hemisphere production is off-season, influencing global prices.
1.2 Production and Harvest Cycles
Melon prices are heavily influenced by supply and the timing of harvests. Most melons have a specific growing season, and any disruptions during this period can affect prices. Melon farming is also highly sensitive to the size of the harvest, and a bumper crop typically results in lower prices, while a smaller-than-expected harvest can push prices upwards.
Geographical Variations: Different regions experience different harvest cycles, which can affect the availability of melons in the market. Countries like the United States, Mexico, and Spain are major melon producers, and price trends are often reflective of harvest outputs in these areas.
Farming Practices and Efficiency: Advances in farming technologies, such as drip irrigation systems and improved crop varieties, can help boost yields and keep prices more stable. Conversely, challenges such as pests, diseases, or resource limitations can lower yields and raise prices.
Enquire For Regular Prices: https://www.procurementresource.com/resource-center/melon-price-trends/pricerequest
1.3 Global Demand and Consumer Preferences
The demand for melons is closely tied to consumer preferences, which can shift due to dietary trends or cultural factors. Increased awareness about healthy eating has led to higher consumption of fruits like melons, which are seen as low-calorie and hydrating snacks. This has especially been the case in markets like the United States and Europe.
Health and Wellness Trends: As consumers become more health-conscious, demand for melons, particularly those with high water content like watermelon, has increased. Melons are also used in various food products, such as smoothies, fruit salads, juices, and snacks, further driving up demand.
Price Sensitivity: While demand remains high for melons, price sensitivity in certain markets can influence purchasing patterns. For instance, consumers may choose cheaper alternatives if melon prices rise sharply during off-seasons or periods of reduced supply.
1.4 Supply Chain and Transportation Costs
Due to their perishability, melons require careful handling during transportation, which can increase costs. Factors such as rising fuel prices, transportation bottlenecks, or disruptions in supply chains can significantly impact melon prices.
Logistical Challenges: Melons need to be transported quickly from farms to markets to avoid spoilage. Any issues in the supply chain, such as port congestion, strikes, or delays, can increase transportation costs and contribute to higher prices in the market.
Cold Storage Requirements: Melons are sensitive to temperature changes and require refrigerated storage to maintain their freshness during transport. Cold storage and energy costs can contribute to higher prices, especially during times of increased global energy prices.
1.5 International Trade and Export-Import Dynamics
Melons are traded internationally, with major exporters including countries like Mexico, the United States, and Spain. Trade policies, tariffs, and other economic factors can influence melon prices, especially in global markets. For example, any trade restrictions or disruptions in exporting countries can reduce the global supply, resulting in price hikes.
Trade Disruptions: Political instability, trade disputes, or changes in export regulations can disrupt melon exports, leading to scarcity and price increases. For example, if a major melon-producing country faces a sudden decrease in exports due to new tariffs, importing countries may experience higher prices as they seek alternative sources.
Currency Exchange Rates: Exchange rate fluctuations can also impact melon prices. A strong currency in exporting countries can make melons more expensive for foreign buyers, while a weaker currency can make exports more affordable but potentially lead to lower profit margins for producers.
2. Historical Melon Price Trends
2.1 Price Stability in Early 2010s
During the early 2010s, melon prices were relatively stable, with minor fluctuations due to seasonal demand and supply factors. The global production of melons was consistent, and weather conditions were largely favourable, ensuring steady prices in many key markets.
- Global Supply and Demand Balance: Supply and demand were well balanced, and the market did not experience significant volatility during this period. Prices remained relatively stable, with the highest prices occurring during the peak summer months when demand was at its highest.
2.2 Price Surges in 2016-2018
Between 2016 and 2018, melon prices saw some fluctuations due to a combination of weather-related disruptions and increased global demand. Extreme weather events such as droughts in key producing regions like the United States and Mexico led to smaller harvests, reducing supply and causing prices to rise.
Extreme Weather Events: A notable drought in California, a major melon-producing state, significantly impacted the 2017 harvest, leading to price increases in both the domestic and international markets.
Increased Global Demand: At the same time, the global demand for melons, especially in North America and Europe, continued to grow, further driving up prices. The increased consumption of health-conscious fruits contributed to the upward trend.
2.3 Volatility in 2020-2022 Due to COVID-19 Pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic caused significant disruptions in the global supply chain, and melon prices were affected by a combination of supply shortages and shifts in consumer demand. During the initial stages of the pandemic, demand for melons fell due to lockdowns and reduced access to retail outlets.
Supply Chain Disruptions: Transport issues, including border closures and shipping delays, resulted in a mismatch between supply and demand. Prices initially fell due to reduced consumption, but as the global supply chain recovered, prices rebounded due to supply shortages caused by earlier disruptions.
Shift to Online Shopping: During the pandemic, online grocery shopping surged, and consumers' shift to purchasing fruits through new channels resulted in price hikes for melons, particularly in markets where fresh fruit availability was constrained.
2.4 Current Price Trends in 2023 and 2024
In 2023, melon prices showed some signs of recovery following the pandemic's disruptions. However, prices remain volatile due to factors like climate change, geopolitical tensions, and economic uncertainty.
Supply Constraints and Inflation: Rising inflation and higher production costs have continued to put pressure on melon prices. Fuel prices, labour shortages, and increasing costs of inputs like fertilisers and pesticides have contributed to upward price trends.
Continued Demand in Key Markets: Despite the challenges, the demand for melons continues to grow in major markets such as the United States, Europe, and parts of Asia. As consumers seek out healthier, hydrating fruits, melon prices are expected to remain relatively stable with periodic spikes depending on weather conditions.
3. Future Outlook for Melon Prices
3.1 Increasing Demand for Healthy Fruits
As consumers continue to focus on health and wellness, the demand for nutrient-dense fruits like melons is expected to remain strong. This trend could result in higher prices, especially in developed markets.
- Expansion of Health Trends: The growing popularity of plant-based and low-calorie diets may further boost melon consumption, driving prices higher due to sustained demand.
3.2 Impact of Climate Change
The ongoing effects of climate change may continue to disrupt melon production in key regions. Unpredictable weather patterns, including severe droughts or heavy rainfall, could lead to inconsistent harvests, further contributing to price fluctuations.
- Water Scarcity: Melon farming is water-intensive, and in regions facing water shortages, production costs are likely to rise, pushing up prices.
3.3 Technological Advancements in Farming
Advancements in agricultural technology, such as improved irrigation systems, pest control, and crop varieties, could help stabilize melon prices by increasing yields and improving fruit quality.
- Precision Agriculture: The adoption of precision farming techniques can help reduce production costs and improve crop resilience, which may mitigate some of the volatility seen in melon prices.
Contact Us:
Company Name: Procurement Resource
Contact Person: Leo Frank
Email: sales@procurementresource.com
Toll-Free Numbers:
- USA & Canada: +1 307 363 1045
- UK: +44 7537171117
- Asia-Pacific (APAC): +91 1203185500
Address: 30 North Gould Street, Sheridan, WY 82801, USA