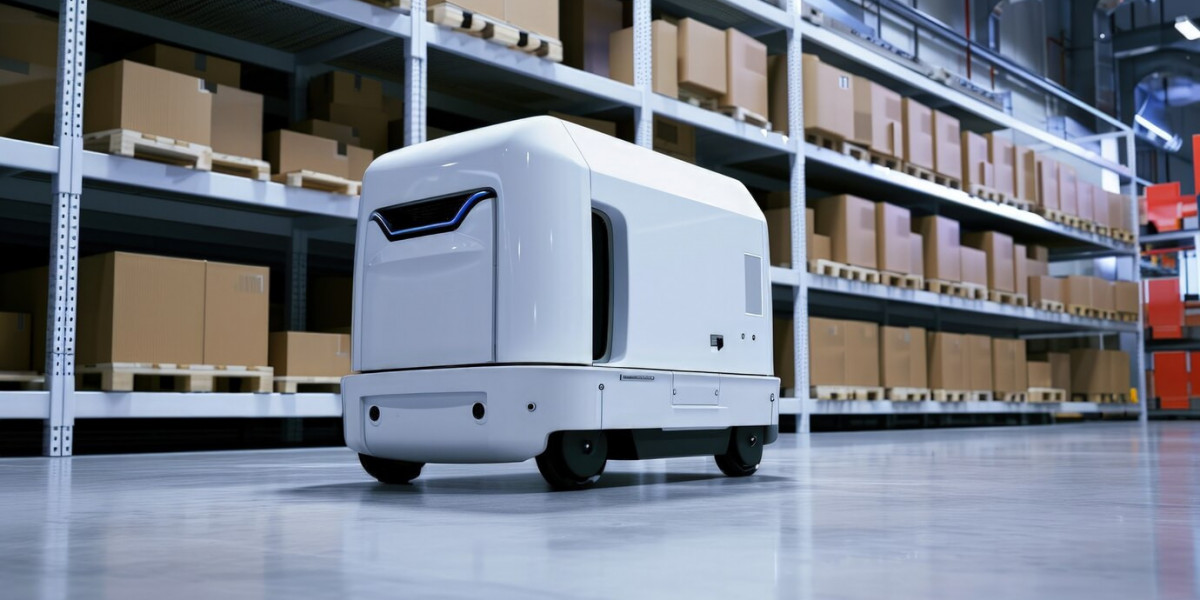
The warehouse automation market is experiencing significant advancements, driven by the need for efficiency, cost reduction, and faster operations. Robotics, artificial intelligence (AI), and Internet of Things (IoT) solutions are transforming warehouse management. However, despite its rapid growth, the industry faces several pain points that hinder widespread adoption. High implementation costs, workforce adaptation challenges, integration difficulties, security concerns, and regulatory constraints are major obstacles. Identifying and addressing these pain points is crucial for businesses aiming to leverage automation for long-term success.
High Investment and Implementation Costs
One of the biggest pain points in warehouse automation is the high cost of investment. Businesses must allocate substantial capital to purchase automated robots, AI-driven software, and advanced warehouse management systems (WMS). The installation, integration, and maintenance of these technologies add further financial burdens. Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) find it particularly challenging to afford automation, leading to slower adoption across the industry.
Workforce Resistance and Skill Gaps
Employees often resist automation due to concerns about job displacement. Many warehouse workers fear losing their roles to robots and AI-powered systems, leading to reluctance in adopting automation. Additionally, warehouse automation requires specialized skills in robotics programming, data analytics, and system troubleshooting, which many existing workers lack. The shortage of skilled professionals in these areas creates a significant barrier to automation implementation.
Integration with Legacy Systems
Many warehouses still operate on outdated legacy systems that are incompatible with modern automation solutions. Transitioning from traditional operations to fully automated processes requires seamless integration, which can be complex and costly. Incompatibility between different software platforms, data management systems, and robotic technologies further complicates the process. Businesses must invest in customized solutions, increasing the cost and time required for implementation.
Regulatory and Compliance Challenges
Warehouse automation is subject to various regulatory and compliance requirements, making implementation more challenging. Labor laws, workplace safety regulations, and data protection policies must be carefully followed when deploying automated systems. Changing regulatory environments across different regions add another layer of complexity, forcing businesses to continuously adapt their automation strategies to remain compliant.
Supply Chain Disruptions and Material Shortages
The warehouse automation market relies on a steady supply of electronic components, sensors, and robotic parts. However, supply chain disruptions caused by economic instability, trade restrictions, and global material shortages can delay automation projects. Businesses must plan for these uncertainties and develop contingency strategies to avoid prolonged automation deployment timelines.
Security Threats and Cyber Risks
With the increasing adoption of cloud-based and IoT-enabled automation, cybersecurity threats have become a critical pain point. Automated warehouses are vulnerable to hacking, malware attacks, and data breaches that can disrupt operations and compromise sensitive information. Businesses must implement strong cybersecurity measures, including firewalls, encryption, and regular system audits, to protect their automation infrastructure.
Technological Constraints and Compatibility Issues
While warehouse automation technology is advancing, some warehouses face limitations in adopting these solutions. Warehouses with complex layouts, fragile goods, or extreme environmental conditions may struggle to find suitable automation systems. Compatibility issues between different automation vendors can also lead to inefficiencies, requiring businesses to invest in tailored solutions that increase costs and complexity.
Sustainability and Environmental Challenges
Although warehouse automation improves operational efficiency, it also presents sustainability challenges. Many automated systems consume significant amounts of energy, increasing carbon footprints. The disposal of outdated automation equipment further contributes to electronic waste. Businesses must balance automation with sustainability by adopting energy-efficient technologies and eco-friendly warehouse practices. However, sustainable automation solutions often come with higher upfront costs, slowing adoption rates.
Strategies to Overcome Key Barriers
Despite these pain points, businesses can implement strategic measures to overcome warehouse automation challenges. Flexible financing models, such as leasing automation equipment, can reduce initial investment burdens. Workforce training and reskilling programs can help employees adapt to automation, addressing resistance and skill shortages. Standardization in automation technologies can improve integration with legacy systems, making the transition smoother. Strengthening cybersecurity protocols and ensuring regulatory compliance will also help businesses mitigate risks and enhance automation adoption.
Conclusion
The warehouse automation market offers numerous benefits, but several pain points hinder its widespread adoption. High investment costs, workforce adaptation issues, integration complexities, regulatory constraints, and cybersecurity risks remain major challenges for businesses. However, companies that proactively address these issues through strategic investments, employee training, and improved security measures will be better positioned for long-term success in an increasingly automated logistics landscape. As technology continues to evolve, businesses that navigate these pain points effectively will gain a competitive edge in the warehouse automation market.