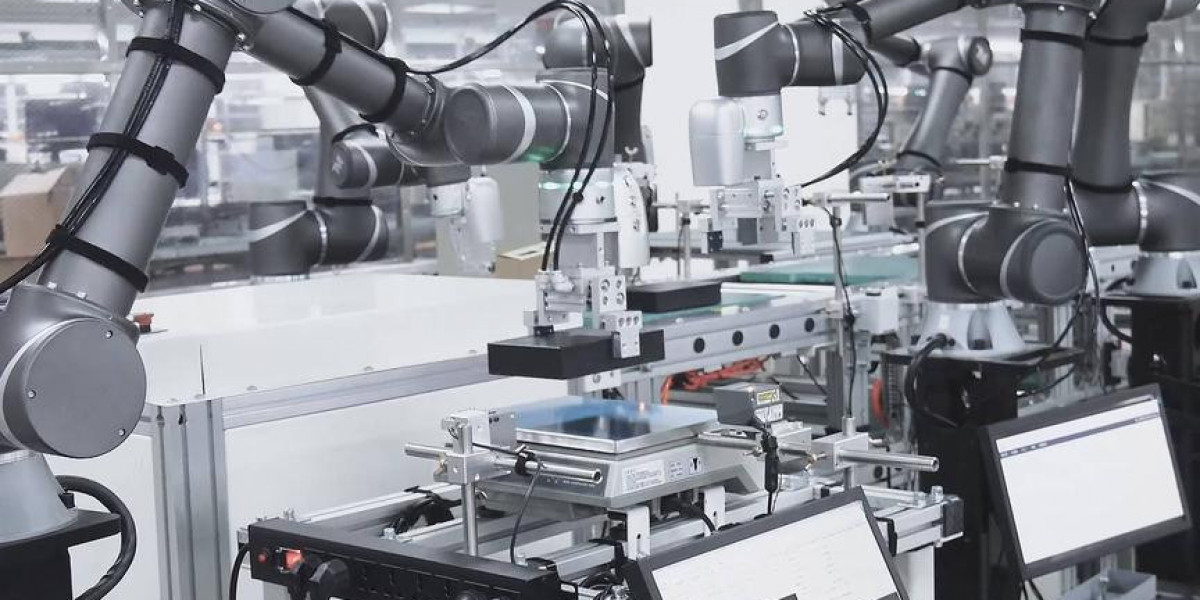
As the collaborative robots market continues to grow, safety remains a critical factor in their development and adoption. Cobots are designed to work alongside human operators in shared spaces, requiring advanced safety features and regulations to ensure that these interactions are both efficient and hazard-free. The integration of safety mechanisms, combined with strict regulatory guidelines, is essential for the successful and widespread use of cobots across various industries.
Safety Features of Collaborative Robots
Safety is at the core of cobot design, as these robots must operate in environments where human workers are present. Unlike traditional industrial robots, which often require safety barriers and restricted areas to function, cobots are engineered to collaborate directly with humans. Several key safety features are incorporated into cobots to facilitate this collaboration:
Force and Torque Sensing
Cobots are equipped with force and torque sensors that allow them to detect physical contact with humans or objects. If a cobot encounters an unexpected force, such as a collision with a person, it can immediately stop or reduce its speed to prevent injury. This adaptive response to contact is essential for safe human-robot interaction, especially in environments where workers are in close proximity to the robot.Speed and Power Limitation
One of the most important safety features of cobots is their ability to limit speed and power. Unlike traditional robots that can operate at high speeds and exert significant force, cobots are programmed to function at slower speeds and lower power levels to minimize the risk of injury. These limitations are often customizable, allowing businesses to adjust the robot’s capabilities according to the specific tasks it performs and the safety requirements of the workspace.Collision Detection and Emergency Stops
Cobots are designed to recognize and respond to unanticipated collisions with objects or humans. This is often achieved through proximity sensors, vision systems, or touch sensors. When a collision occurs, the cobot can automatically stop or back away, reducing the risk of harm. Emergency stop buttons and safety protocols are also integrated into cobots, enabling immediate shutdown in the event of an unexpected hazard.Safety-rated Monitored Stops (SRMS)
In some cases, cobots are programmed to enter a "monitored stop" mode, which allows the robot to pause its operations while still being able to sense human presence. This feature enables cobots to stop immediately when a person is detected, and once the person moves away, the cobot resumes its tasks.
Regulations Governing Collaborative Robots
While safety features are built into cobots, they must also comply with industry regulations and standards to ensure their safe deployment. These regulations are set by various national and international organizations to provide guidelines for the design, operation, and safety of robotic systems in human-robot collaborative environments.
ISO/TS 15066
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has developed the ISO/TS 15066 standard, which specifically addresses the safety requirements for collaborative robots. This standard outlines the permissible limits for robot speed, force, and power, as well as the necessary safety mechanisms, such as sensors and emergency stop functions. It also provides guidelines for risk assessments, which help manufacturers and businesses evaluate the safety of their cobots in different operational settings.CE Marking and Compliance
In Europe, cobots must comply with the CE marking requirements to be legally sold and operated within the European Union (EU). The CE mark indicates that the cobot has been assessed for safety and conforms to the EU’s health, safety, and environmental protection standards. This includes compliance with the Machinery Directive and other relevant safety regulations.OSHA Guidelines
In the United States, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) provides guidelines for the safe operation of robots in industrial environments. While OSHA does not have specific regulations for cobots, it mandates that companies assess and mitigate any potential hazards associated with robotics. Businesses must ensure that cobots are integrated into their workflows in a way that does not jeopardize worker safety.
Future Developments in Cobot Safety
As cobots become more advanced and their use expands across different sectors, safety regulations and features will continue to evolve. Future cobots are expected to incorporate even more sophisticated safety systems, such as advanced vision and AI-powered sensors, which can predict and react to potential risks before they happen. Additionally, regulatory bodies are likely to update safety standards to account for new technologies and work environments, ensuring that cobots can be safely integrated into a wider range of applications.
Conclusion
Safety is a fundamental aspect of the collaborative robots market, ensuring that these robots can operate safely alongside human workers. With built-in safety features such as force sensors, speed limitations, and emergency stop mechanisms, cobots are designed to minimize risks. Regulatory standards such as ISO/TS 15066 and CE marking provide the framework for safe cobot deployment, giving businesses confidence in the safety of these advanced automation solutions. As the market continues to grow, the development of enhanced safety features and evolving regulations will further promote the adoption of cobots in diverse industries, making them a valuable tool for businesses looking to improve efficiency while maintaining a safe work environment.