Introduction
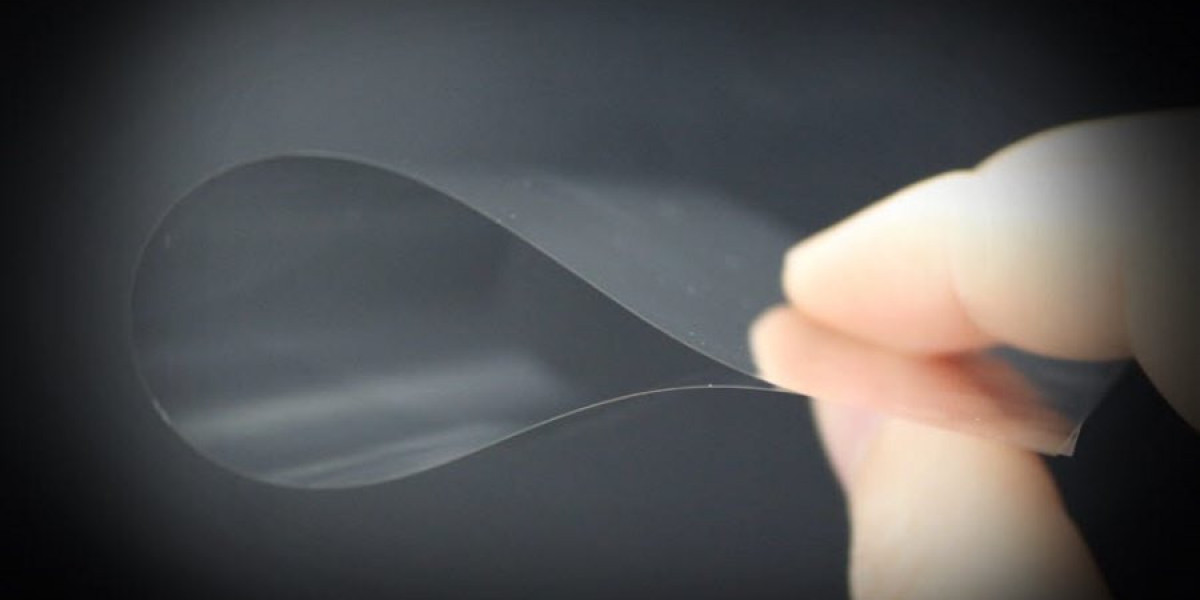
As industries increasingly prioritize sustainability, ultra-thin glass is emerging as an eco-friendly alternative in various applications. With its lightweight, recyclable, and energy-efficient properties, ultra-thin glass market is contributing to reducing environmental footprints across sectors such as consumer electronics, automotive, and construction. This article explores the sustainability aspects of ultra-thin glass, its environmental benefits, and challenges in making its production more sustainable.
Environmental Benefits of Ultra-thin Glass
1. Energy Efficiency in Manufacturing and Usage
Ultra-thin glass requires less raw material compared to conventional glass, reducing energy consumption in production.
Its lightweight nature reduces transportation emissions and enhances fuel efficiency in industries like automotive and aerospace.
In consumer electronics, ultra-thin glass contributes to energy-efficient displays and solar panels, leading to reduced power consumption.
2. Recyclability and Waste Reduction
Ultra-thin glass is fully recyclable, minimizing waste generation and reducing landfill accumulation.
Manufacturers are investing in closed-loop recycling processes to enhance material reuse and sustainability.
Recycling ultra-thin glass contributes to a circular economy, reducing the need for new raw materials.
3. Sustainable Applications in Green Architecture
Ultra-thin smart glass is increasingly used in eco-friendly buildings for energy-efficient windows and facades.
Smart glass technology, such as electrochromic glass, reduces heating and cooling costs by dynamically adjusting transparency.
The use of ultra-thin glass in photovoltaic solar panels improves energy efficiency and renewable energy adoption.
4. Reduction in Harmful Emissions and Resource Usage
The production of ultra-thin glass requires fewer raw materials, leading to lower carbon emissions.
Advancements in manufacturing techniques, such as chemical strengthening, reduce the need for energy-intensive processes.
Ultra-thin glass coatings enhance product durability, reducing the frequency of replacements and material waste.
Challenges and Solutions in Sustainable Production
High Energy Consumption in Processing: Although ultra-thin glass requires less raw material, its manufacturing still demands high energy inputs. Investing in renewable energy sources for production can mitigate this impact.
Limited Recycling Infrastructure: Developing advanced recycling technologies and policies can enhance the recovery and reuse of ultra-thin glass materials.
Chemical Treatments and Coatings: Some chemical treatments used to strengthen ultra-thin glass pose environmental concerns. Research into eco-friendly strengthening techniques is crucial for sustainability.
Cost of Sustainable Materials: The transition to greener production methods may increase costs initially, but long-term benefits in sustainability and efficiency outweigh the expenses.
Future Outlook
Advancements in green manufacturing processes will reduce energy consumption and carbon emissions in ultra-thin glass production.
Increased adoption of sustainable construction materials will drive demand for ultra-thin glass in smart buildings and renewable energy applications.
Collaboration between governments and industry leaders will foster regulations and incentives for sustainable ultra-thin glass development.
Breakthroughs in recyclable ultra-thin glass innovations will further enhance its role in achieving circular economy goals.
Conclusion
The ultra-thin glass market is evolving to align with global sustainability trends, offering significant environmental benefits while addressing production challenges. By prioritizing energy efficiency, recyclability, and eco-friendly applications, ultra-thin glass is set to play a vital role in reducing carbon footprints across industries. As research and technological advancements continue, ultra-thin glass will contribute to a more sustainable future, making it a key material in green innovation and environmental conservation.