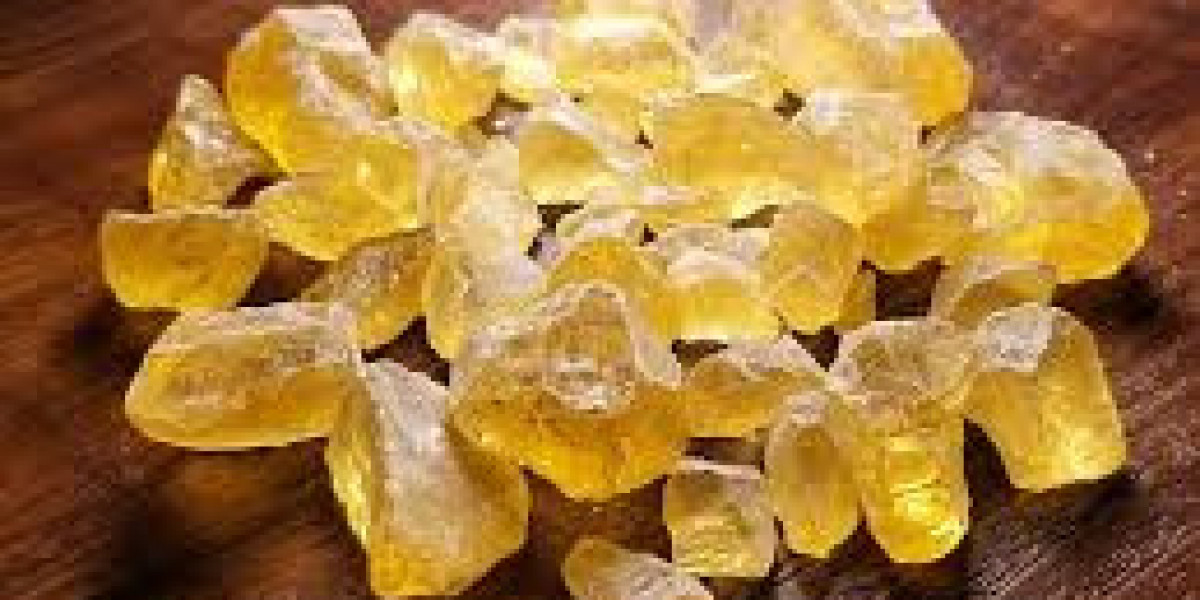
Gum rosin, derived from pine trees, has long served as a critical raw material across a wide range of industries, including adhesives, inks, rubber, paints, and coatings. Despite its natural origin and wide industrial application, the global gum rosin market is currently experiencing notable constraints that are impeding its expansion. These market restraints stem from environmental, economic, and geopolitical factors, each playing a significant role in shaping the future trajectory of the industry.
1. Raw Material Dependency and Supply Chain Instability
One of the most significant restraints in the gum rosin market is its heavy dependency on natural sources, particularly pine trees. The majority of gum rosin is produced in countries such as China, Indonesia, Brazil, and India, where pine tree availability and labor-intensive tapping processes are central to production. However, deforestation regulations, land-use changes, and climate change are reducing the accessibility and yield of pine trees, directly affecting gum rosin supply.
Furthermore, unpredictable weather patterns can hinder resin collection, further contributing to inconsistent raw material availability. When coupled with transportation and logistic challengesespecially in remote forest areasthe market becomes vulnerable to frequent supply disruptions.
2. Fluctuating Prices and Competitive Alternatives
Gum rosin prices are highly sensitive to supply-demand dynamics, currency exchange rates, and changes in the global economy. This volatility can make it difficult for manufacturers and downstream industries to maintain cost-effective production lines. In periods of raw material shortages, gum rosin prices can skyrocket, prompting industries to seek cheaper, more stable synthetic alternatives.
For instance, petroleum-based resins and tall oil rosin (a byproduct of the paper industry) are increasingly preferred due to their lower cost and more consistent availability. This shift to synthetic or alternative products places pressure on gum rosin producers and dampens long-term demand.
3. Environmental Regulations and Sustainability Pressures
The increasing focus on sustainability and environmental preservation presents a double-edged sword for the gum rosin market. While gum rosin is a natural, biodegradable substance, its harvesting process can have a negative impact on forest ecosystems if not managed sustainably. Many governments are tightening forestry regulations, implementing strict environmental standards, and limiting resin tapping to protect biodiversity.
Complying with these regulations often requires investment in more sustainable harvesting practices and certification, which can raise production costs and reduce profit marginsparticularly for small-scale producers in developing countries.
4. Labor-Intensive Production and Declining Workforce
Resin tapping remains a labor-intensive process, often carried out in rural areas with limited access to modern agricultural technology. As younger generations move toward urban jobs and away from forest-based labor, the industry is facing a declining workforce. This shortage of skilled labor directly affects production efficiency and volume.
The lack of mechanization also contributes to inconsistent resin quality, which can affect downstream processes and product performance. Without significant technological upgrades or labor incentives, the industry may struggle to sustain productivity.
5. Geopolitical Tensions and Export Barriers
The gum rosin trade is sensitive to global geopolitical dynamics. Export restrictions, tariffs, and trade barriersespecially involving major producers like Chinacan disrupt global supply chains. Additionally, political instability in resin-producing countries may lead to unreliable exports and hinder international business relationships.
Trade conflicts, such as the US-China tariff war, have in the past caused significant shifts in global gum rosin pricing and availability. These uncertainties limit foreign investment and make long-term strategic planning difficult for market players.
Conclusion
The gum rosin market, while essential for many industrial processes, is not without its challenges. Environmental sustainability concerns, fluctuating prices, labor issues, and geopolitical instability all contribute to significant restraints that limit its growth. To maintain relevance in an increasingly competitive and eco-conscious world, gum rosin producers must adopt innovative approaches, embrace sustainable practices, and diversify their supply chains to ensure resilience and continuity.