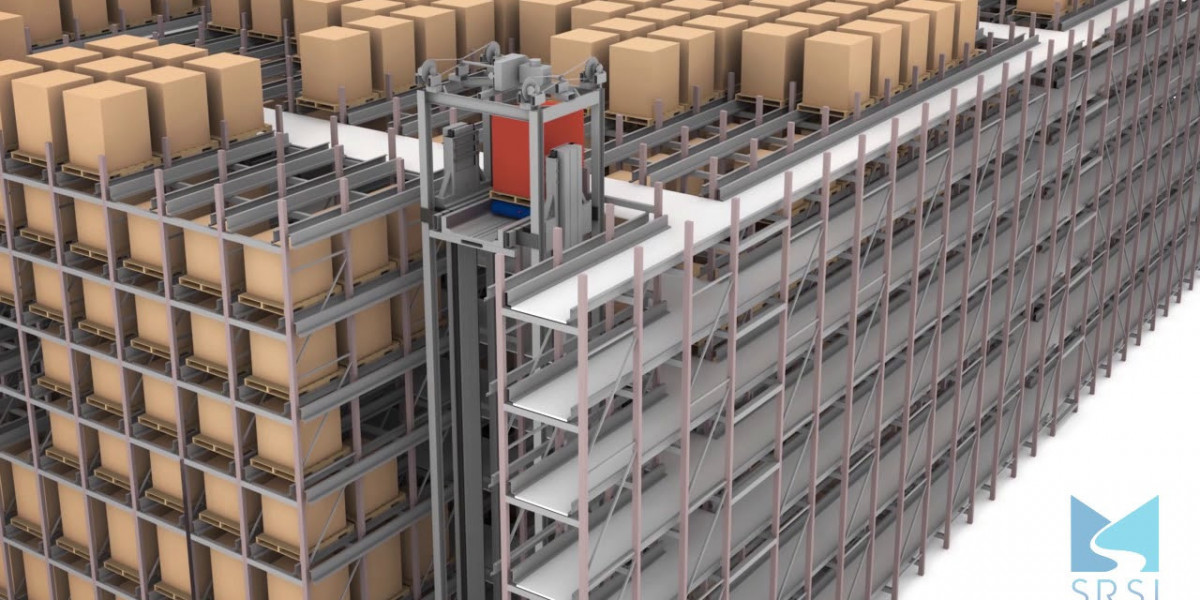
Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (ASRS) have witnessed substantial growth over recent years due to their ability to streamline warehouse and inventory management, enhance efficiency, and reduce human labor. However, despite their promising benefits, the growth of the ASRS market is hindered by a range of challenges that impact the adoption and expansion of these systems. These restraints are multifaceted and encompass financial, technical, operational, and environmental factors. Below are the key challenges that could limit the widespread adoption and growth of the ASRS market.
1. High Initial Investment Costs
One of the most significant restraints on the growth of the ASRS market is the high initial capital expenditure required for installation and integration. ASRS solutions often require substantial upfront investments in hardware, software, and infrastructure. Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) may find it difficult to justify such large capital expenditures, especially when they are uncertain about the return on investment (ROI). The cost of the systems includes robotic equipment, conveyors, storage racks, sensors, control systems, and software solutions. Additionally, installation and customization costs, as well as the expenses associated with employee training and system integration, add to the overall financial burden. This makes ASRS more appealing to larger organizations with greater financial resources, leaving smaller players hesitant to make the investment.
2. Complexity in System Integration
ASRS solutions must be integrated with existing supply chain and warehouse management systems (WMS) to function optimally. This integration can be highly complex and may require significant adjustments to legacy systems. Compatibility issues between older systems and newer automated solutions can lead to delays in implementation and increased costs. In some cases, a complete overhaul of the existing infrastructure may be necessary to accommodate an ASRS, further elevating the overall investment. Additionally, integrating various components—such as automated guided vehicles (AGVs), robotics, and software—requires specialized knowledge, and any errors or incompatibilities during the process could disrupt operations and lead to inefficiencies.
3. Limited Flexibility in Handling Diverse Products
ASRS are often designed to work efficiently with a particular type of product or within a specific operational environment. While they excel in applications requiring high-density storage and rapid retrieval, they can face difficulties when dealing with diverse product types, especially those that are fragile, perishable, or of irregular sizes and shapes. Customizing an ASRS to handle a wider variety of goods can be costly and technically challenging. This lack of flexibility can be a major barrier for industries that deal with highly varied inventories, such as food and beverage or pharmaceuticals, where the nature of the products may require different storage conditions or handling processes.
4. Technological Challenges and Dependence on Software
The functionality of ASRS depends heavily on the software that controls the entire system. Issues such as software bugs, glitches, or system failures can have a profound impact on the efficiency of the warehouse operations. For instance, any software malfunction can lead to incorrect retrievals, damaged goods, or a halt in the entire operation. Furthermore, regular software updates, maintenance, and troubleshooting are required to keep the system functioning at optimal levels, which adds to the operational burden. A malfunction in the control system or a failure to update software regularly can result in costly downtime, which can severely affect business operations.
5. Space and Environmental Limitations
While ASRS solutions are designed to maximize space efficiency, they still require a certain amount of physical space for installation and operation. In densely populated regions or in warehouses with space constraints, it may be difficult to accommodate large ASRS units. Additionally, some ASRS solutions, particularly those involving high-speed robotic arms or automated conveyors, generate noise, heat, or vibrations, which can impact the working environment. For industries operating in controlled environments, such as the pharmaceutical or food sectors, these systems may need additional modifications to meet stringent environmental regulations, further increasing costs and complexity.
6. Maintenance and Operational Downtime
The reliance on advanced mechanical and electronic components in ASRS solutions makes them prone to wear and tear over time. While these systems are designed to be durable, they still require regular maintenance to ensure they continue operating efficiently. The need for routine checks, repairs, and part replacements can lead to downtime, which in turn disrupts operations and affects productivity. In the event of a breakdown or malfunction, the system may need to be taken offline, requiring costly repairs or the deployment of backup systems. This downtime can cause delays in order fulfillment, impacting customer satisfaction and leading to lost revenue.
7. Resistance to Change and Workforce Concerns
Implementing ASRS often leads to workforce restructuring, as the automation reduces the need for manual labor in warehousing and storage operations. This can lead to resistance from employees and labor unions who fear job displacement. Additionally, employees may need to be retrained to manage and maintain the new automated systems, which can be time-consuming and costly. This resistance to change can delay the adoption of ASRS, particularly in organizations where the workforce is hesitant or where labor-related concerns dominate.
8. Scalability Issues
Although ASRS can handle large volumes of goods, scaling these systems can be a complex process. As businesses grow and their storage and retrieval needs increase, the ASRS may require significant adjustments or expansions to accommodate the higher throughput. Scaling an ASRS system often involves adding more robots, conveyors, and racks, and these upgrades can be both expensive and time-consuming. The challenge lies in ensuring that the system remains adaptable to the company’s evolving needs without significant additional investments or operational disruptions.
Conclusion
The growth of the Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems market is undoubtedly hindered by several factors, including high costs, integration complexities, product handling limitations, technological dependencies, and workforce concerns. While these systems offer numerous advantages in terms of efficiency, accuracy, and speed, overcoming these challenges is crucial for their widespread adoption, particularly in small to mid-sized enterprises. Addressing these issues will require continued technological innovation, cost reduction strategies, and improved system integration solutions to unlock the full potential of ASRS in various industries.
read more:
| https://www.pristinemarketinsights.com/automated-storage-and-retrieval-systems-market-report |